Lecture 21: Files |
Lecture 21: Files |


 Today
we are going to learn how to read from files and write to file. As an
example
we will only learn how to read and write text files, files where the
infomation
is stored in ASCII format. Such files differ from binary format because
they are also readable by humans. We already are using with text files,
because all our programs written in the practical lessons are of this
type.
Today
we are going to learn how to read from files and write to file. As an
example
we will only learn how to read and write text files, files where the
infomation
is stored in ASCII format. Such files differ from binary format because
they are also readable by humans. We already are using with text files,
because all our programs written in the practical lessons are of this
type.
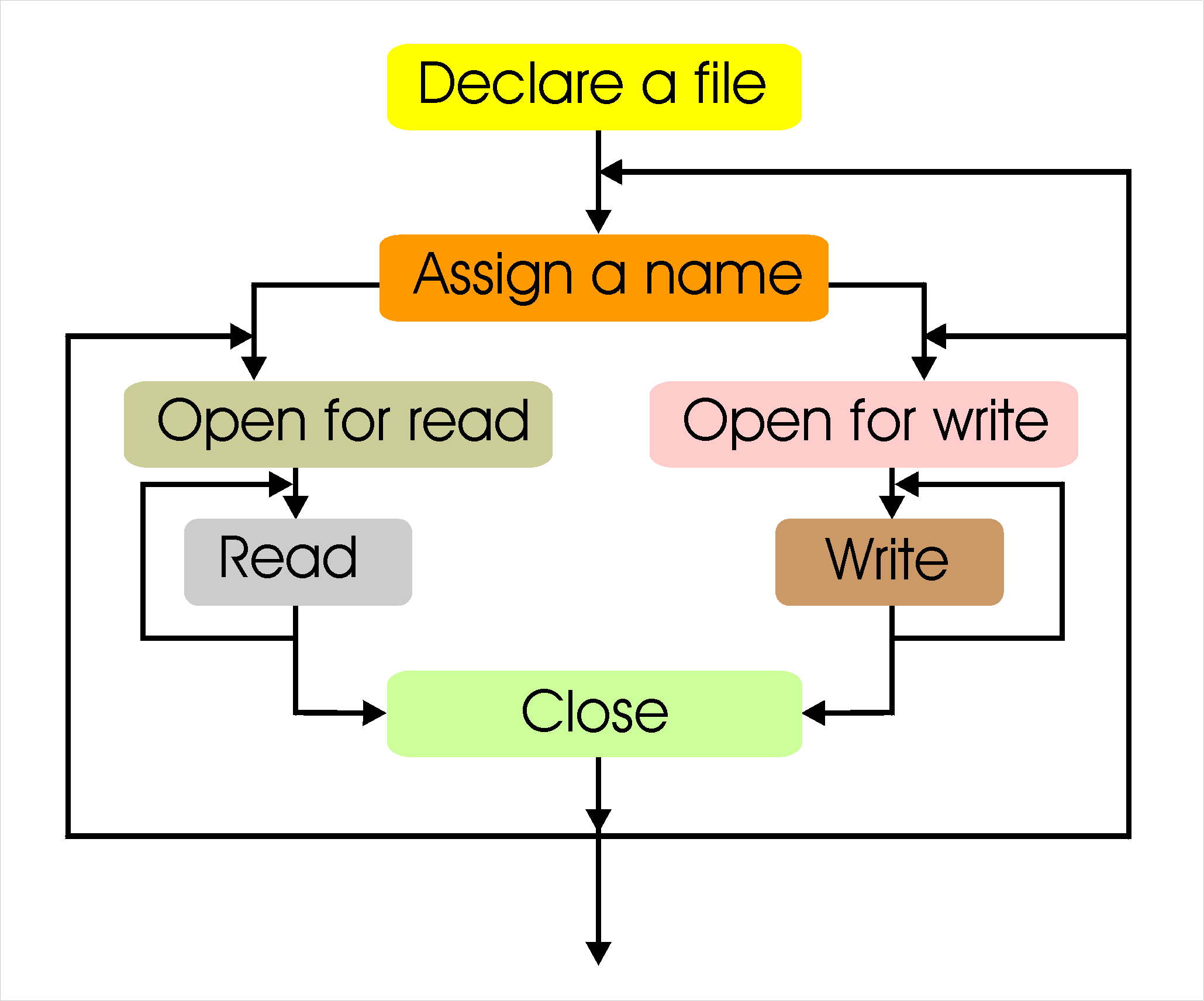
| Var text
Assign Rewrite Reset Close Read, ReadLn Write, WriteLn Eol, Eof |
| Var filehandle: text; |
With filehandle the logical
name
of the file. This is not equal to the actual name of the file, as we
will
see in a moment. The place to declare this is together with the files.
Example:
Var f: text;
| Assign(filehandle,filename); |
The filehandle is the one
declared
above and the filename is a
string
(constant or variable) containing the name of our file. For example:
Assign(f, 'MYFILE.TXT');
ReadLn(s);
Assign(f, s);
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
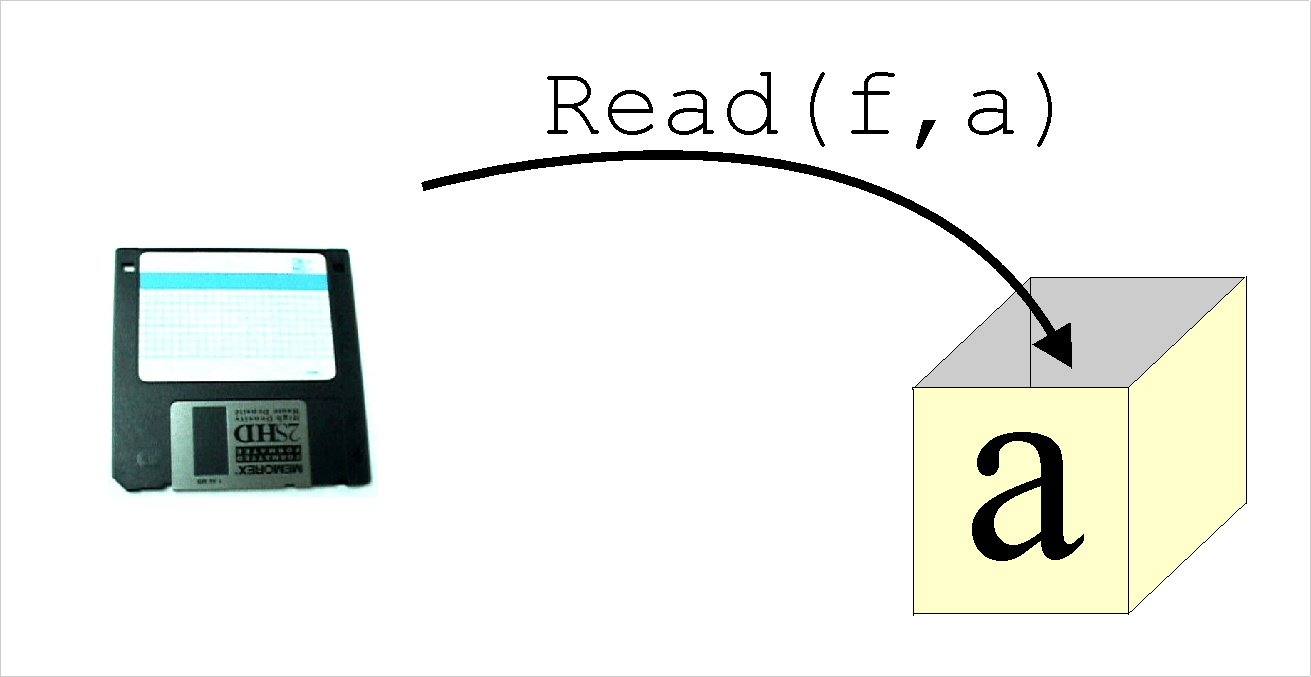
Note that we can only use the Read
and ReadLn instructions for
files
that have previously been opened for input and Write
and WriteLn are only to be used
for
files opened for output. Examples:
WriteLn(f, r:0:2);
ReadLn(f, opcao);
 |
 |
|
|
|
| Close(filehandle); |
Example:
While NOT Eof(f) do
ReadLn(s);
which will read from the file until the end of
the file is encountered.
| code | screen | file TEST.TXT
after running the program |
| PROGRAM WithFileOutPut;
Var f: text;
begin
|
Name of File:
TEST.TXT |
1 Hello
2 Hello 3 Hello 4 Hello 5 Hello 6 Hello 7 Hello 8 Hello 9 Hello 10 Hello |
| code | screen | file TEST.TXT before
running the program |
| PROGRAM WithFileInPut;
Var f: text;
begin
|
Name of File:
TEST.TXT 1 Hello 2 Hello 3 Hello 4 Hello 5 Hello 6 Hello 7 Hello 8 Hello 9 Hello 10 Hello |
1 Hello
2 Hello 3 Hello 4 Hello 5 Hello 6 Hello 7 Hello 8 Hello 9 Hello 10 Hello |